In the article Bioplastic classification, we learned about the definition of bioplastics and the distinction between biobased and biodegradable plastics. This article will try to explain the concept of bioplastic solutions further and dive deeper into its production, advantages and disadvantages, applications, and end-of-life of bioplastics.
Download our e-book about the sustainable materials we use in our manufacturing process >>
Global production of bioplastic
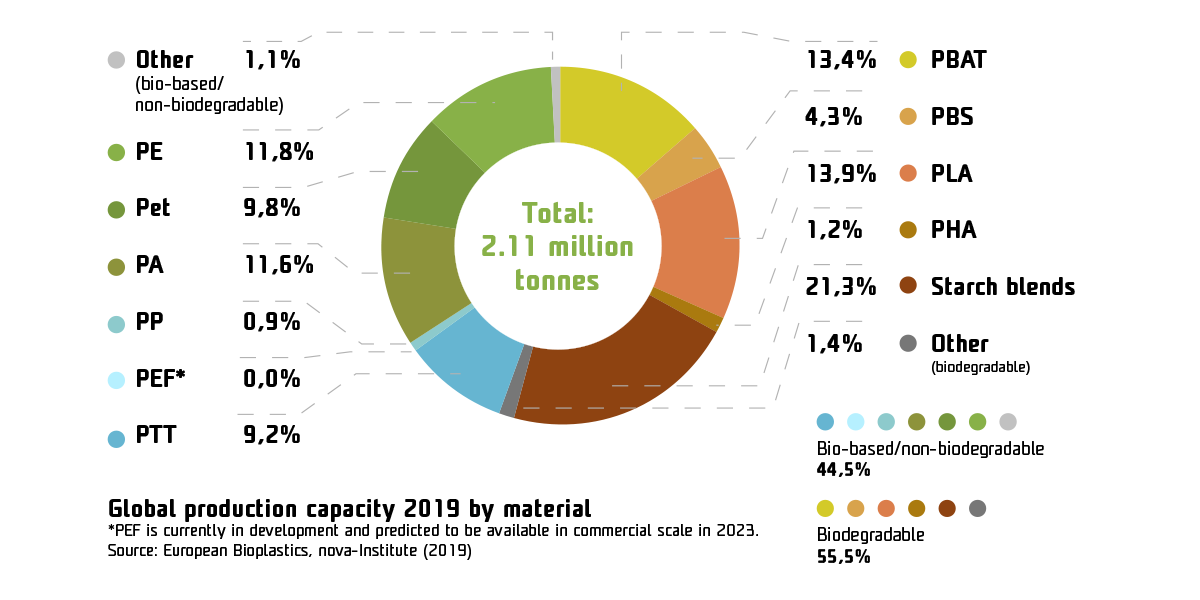
While global production of plastics amounts to a staggering 367 million tons annually, sustainable materials as bioplastics - bioplastic solutions - have only recently made their way into the market. Despite the increased environmental awareness, bioplastic still accounts for only about 0.6% (2.1 million tons) of total plastic production. However, the production of bioplastics is expected to experience steady growth to about 2.9 million tons in 2025. About 44.5% of all bioplastics produced are exclusively biobased, with the remainder composed of various types of biodegradable plastics that can be either fossil-based or bio-based. Starch blends have the largest share (21.3 %), followed by polylactic acid (PLA) (13.9 %) and polybutylene adipate terephthalate (PBAT) (13.4 %), which are mainly used in packaging applications.
Advantages and disadvantages of bioplastic solutions
Bioplastic solutions have significant advantages over conventional plastics in the sense that they reduce greenhouse gas emissions and the depletion of fossil resources. As such, bioplastics contribute to our ambitious goal of becoming a carbon-neutral society, not dependant on fossil resources. Unfortunately, bioplastics may also have worse environmental impacts than conventional plastics in some aspects due to the intense use of fertilizers in the cultivation of renewable raw materials used for bio-based plastic production. Therefore, comparing the environmental impact of conventional and bioplastic solutions is not a completely black and white story but instead depends on which environmental impact we consider to be more important.
An important advantage of biodegradable plastics is their ability to be broken down into non-harmful compounds, reducing the damage caused by plastics when they are unintentionally released into the environment. Even though the damage is significantly reduced because biodegradable plastics decompose much faster than conventional plastics, it is still a relatively slow process, so care must be taken to dispose of plastic waste responsibly. Biodegradability is also a helpful feature in various biomedical applications, where they are used for the controlled release of drugs and various therapeutic devices, such as implants and scaffolds for tissue engineering. While non-biodegradable bio-based plastics have similar physical properties to their fossil-based counterparts, the physical properties of biodegradable plastics are generally inferior compared to conventional plastics.
Applications of bioplastic solutions
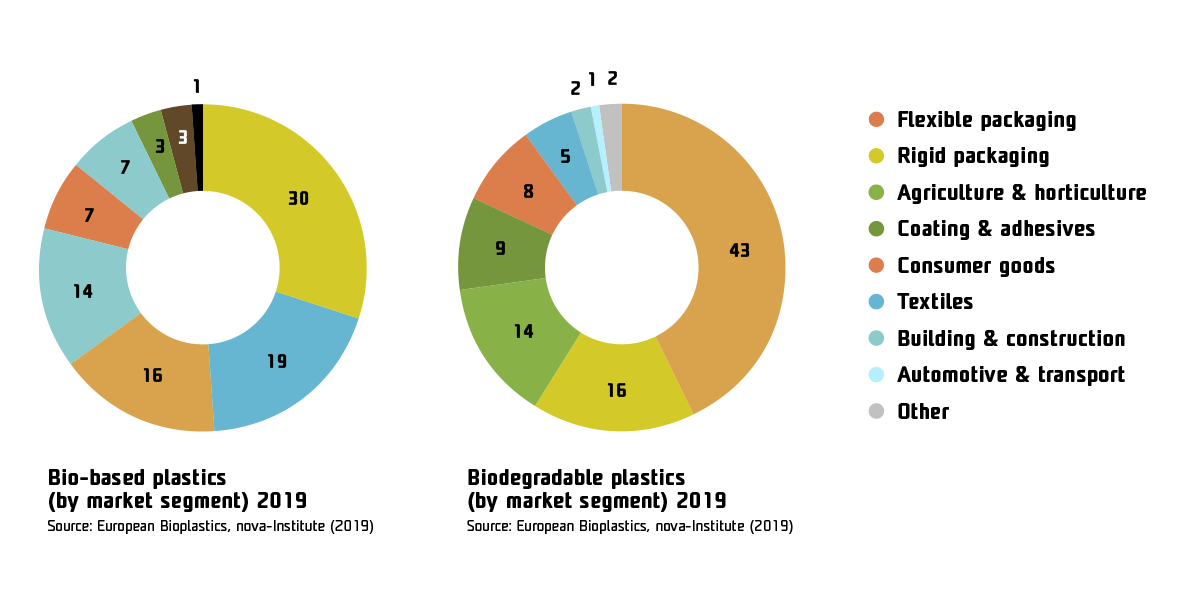
Bioplastics solutions are being used in an increasingly wide range of applications, from packaging, agriculture, consumer goods, textiles, buildings, furniture, electronics, medical, transportation, and other segments. The largest share of bioplastics applications can be found in packaging, where more than 53 % of all bioplastics produced are used. While both bio-based and biodegradable plastics are used in most of the above applications, their market segmentation differs significantly. Biodegradable plastics are predominantly used in packaging applications, while bio-based plastics have a comparatively larger share in the production of various durable goods.
End of life
Efficient waste management is essential to achieve resource efficiency and meet the goals of the circular economy. A large proportion of non-biodegradable biobased plastics such as polyethylene and polyethylene terephthalate can be efficiently mechanically recycled in already established recycling streams, as these types of plastics have the same composition as their fossil-based counterparts. Other types of bioplastics can also be mechanically recycled but suffer from the lack of established recycling streams as they are produced in small quantities. In case biobased plastics cannot be reused or recycled, they can be used as a renewable energy resource through various waste-to-energy technologies.
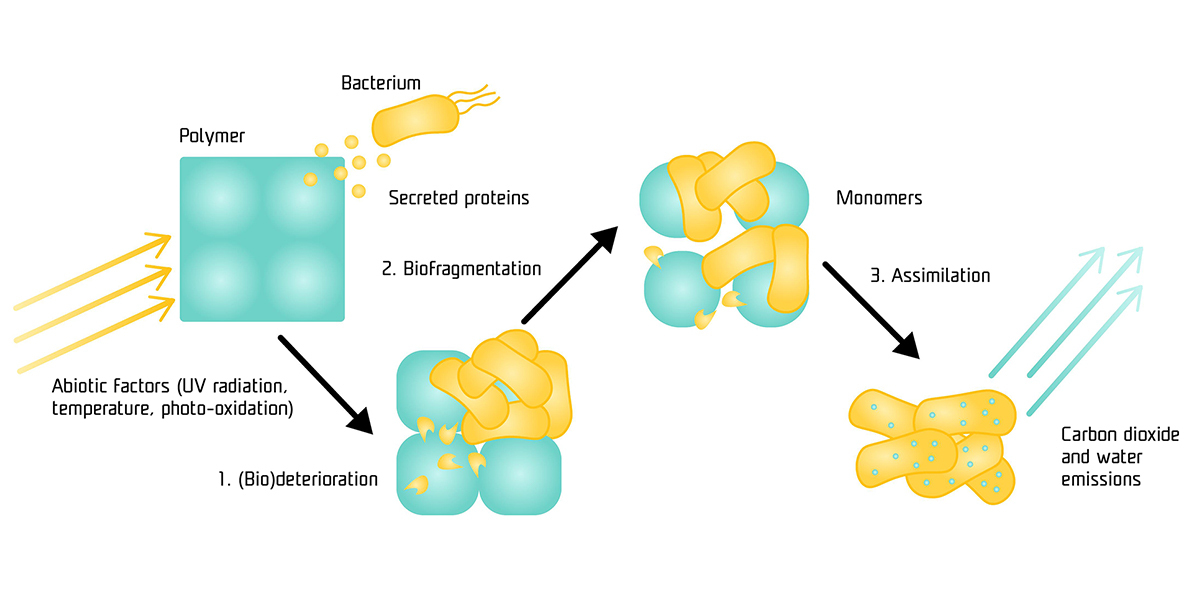
Biodegradable plastics can be subjected to a biodegradation process. With the help of microorganisms, they first break down into smaller parts, then into monomers and finally into biomass, carbon dioxide and water.
Biodegradation provides an additional waste treatment option that is particularly useful in bioplastic solutions such as compostable biowaste bags, food packaging, and cutlery. These products can be disposed of with organic waste and turned into valuable compost in industrial composting facilities.
Find out more about how we incorporate sustainable materials into our production process. Fill in the form and download the e-book with educational content.


